Using catalysts in RTO: a wise investment
Converting regenerative thermal oxidizers to regenerative catalytic oxidizers can create a 60%-100% reduction in energy consumption. Furthermore, coupling RTO with catalysts can yield a significant return on investment.
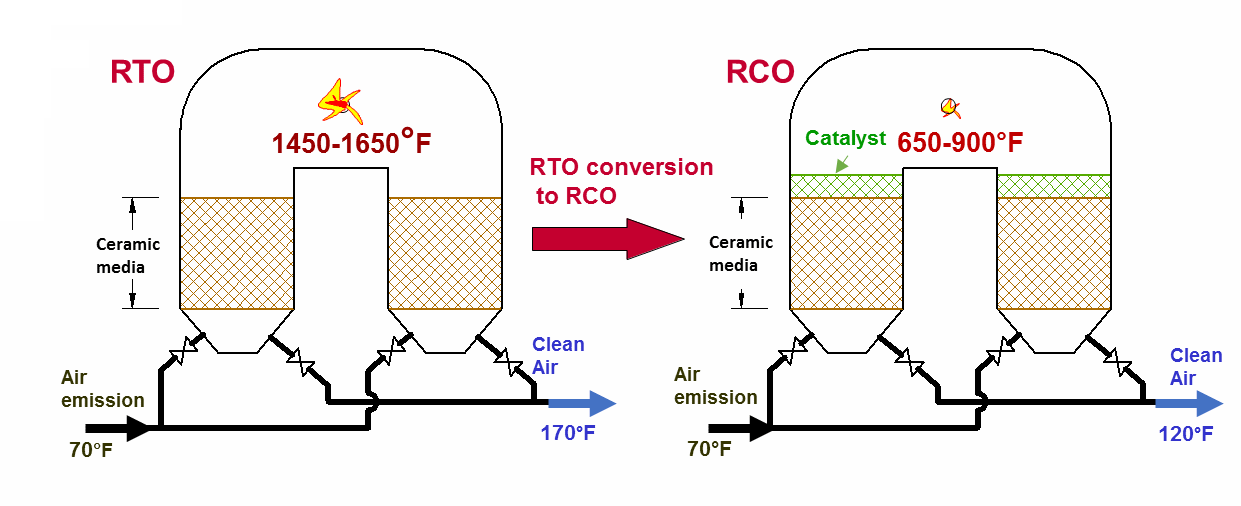
Using catalysts in regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTO) or conversion of RTO to regenerative catalytic oxidizer (RCO) changes the nature of chemical process. In the RCO, the destruction of VOCs takes place within the bed of catalyst, rather than the space of the combustion chamber. The catalyst improves rate of oxidation of VOC, which transfers to much lower temperature for VOC removal. Typically, the temperature is reduced from 1400-1650°F (750-900°C) in RTO to 650-900°F (350-500°C) in RCO. Consequently, the fuel consumption is reduced by 60%-100%. Depending on the price of natural gas, catalyst service time and other factors, the fuel savings in RCO may enable a substantial return on investment.
The existing RTO can be easily converted to RCO. The only difference is that the RCO includes shallow beds of catalyst loaded on top of ceramic media in each heat-exchange canister.
Time of catalyst service depends on catalyst type and quantity and presence and concentrations in air emissions of sulfur, halogens, silicon, phosphorus, metals and other catalyst contaminants. In many applications, 5-7 years can be achieved.